Content
- 1 Understanding Abrasion Resistant Coating and Its Core Purpose
- 2 How Abrasion Resistant Coatings Reduce Surface Wear
- 3 Types of Abrasion Resistant Coating Materials
- 4 Performance Factors That Influence Coating Effectiveness
- 5 Typical Applications of Abrasion Resistant Coatings
- 6 Comparing Coated and Uncoated Surfaces
- 7 Practical Considerations When Selecting a Coating
- 8 Conclusion
Understanding Abrasion Resistant Coating and Its Core Purpose
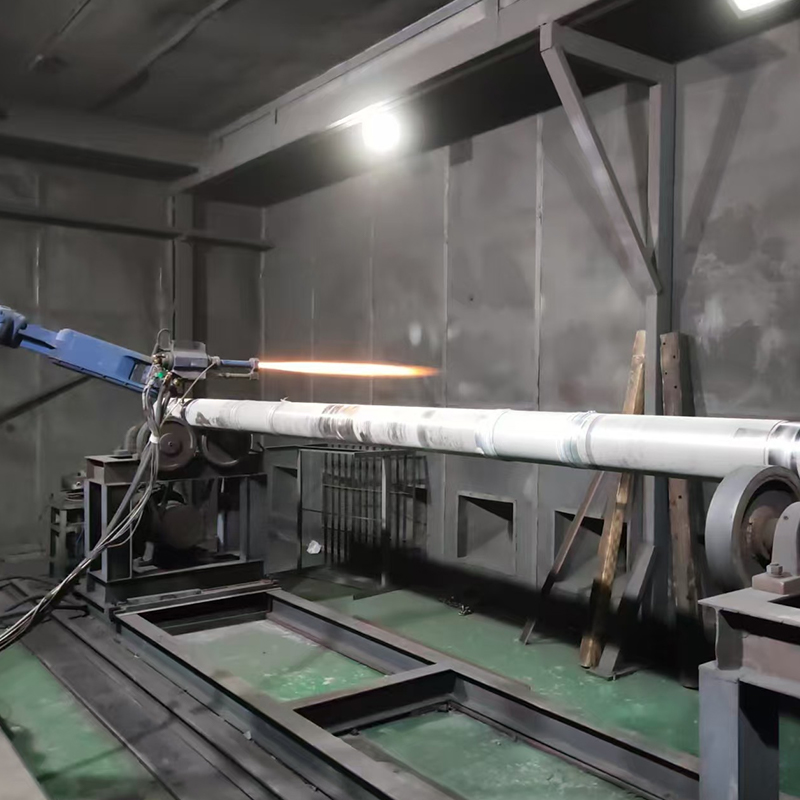
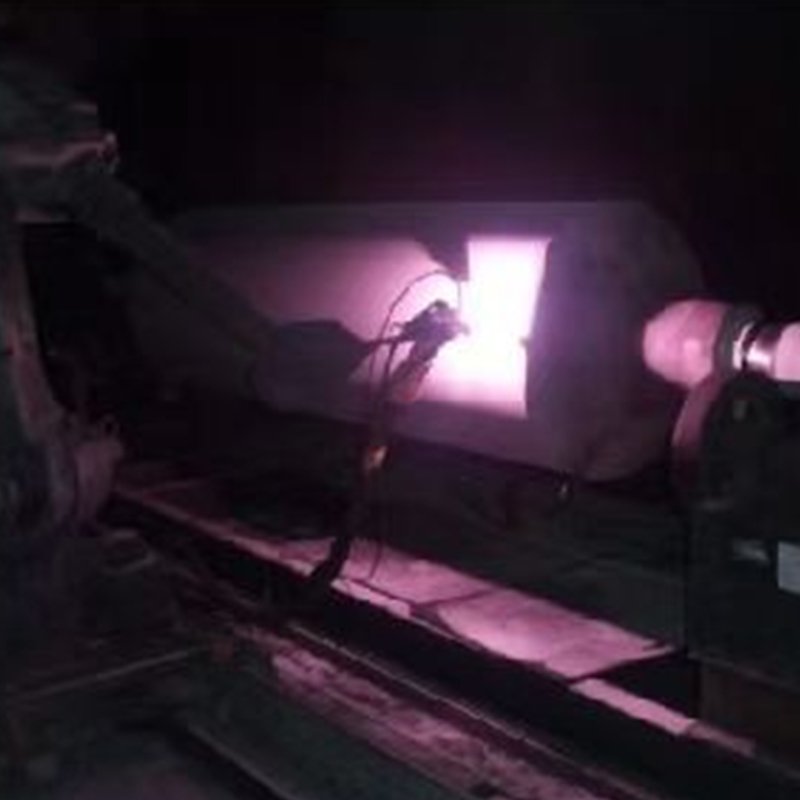
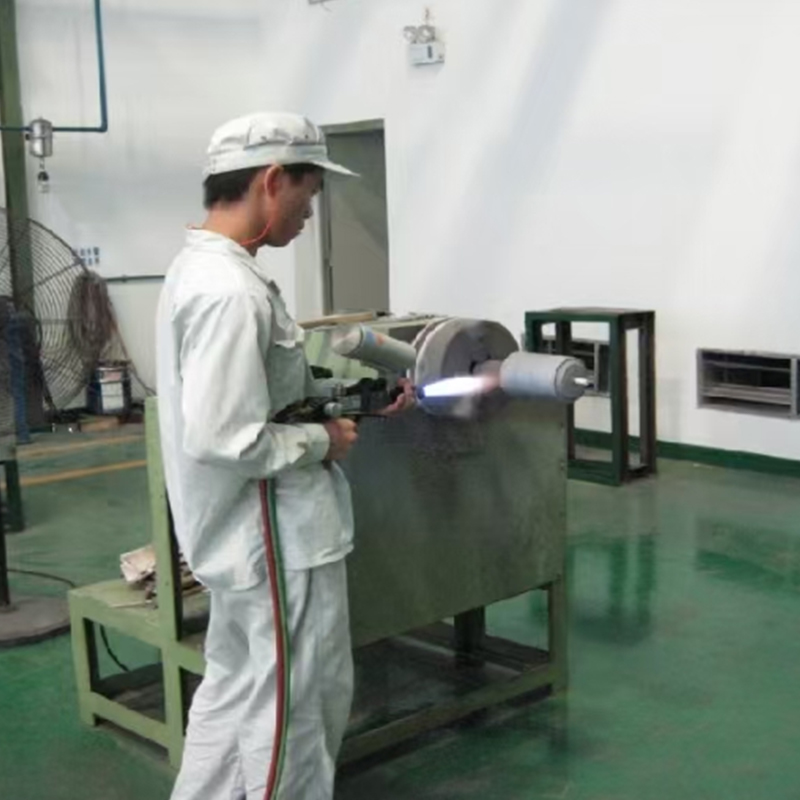
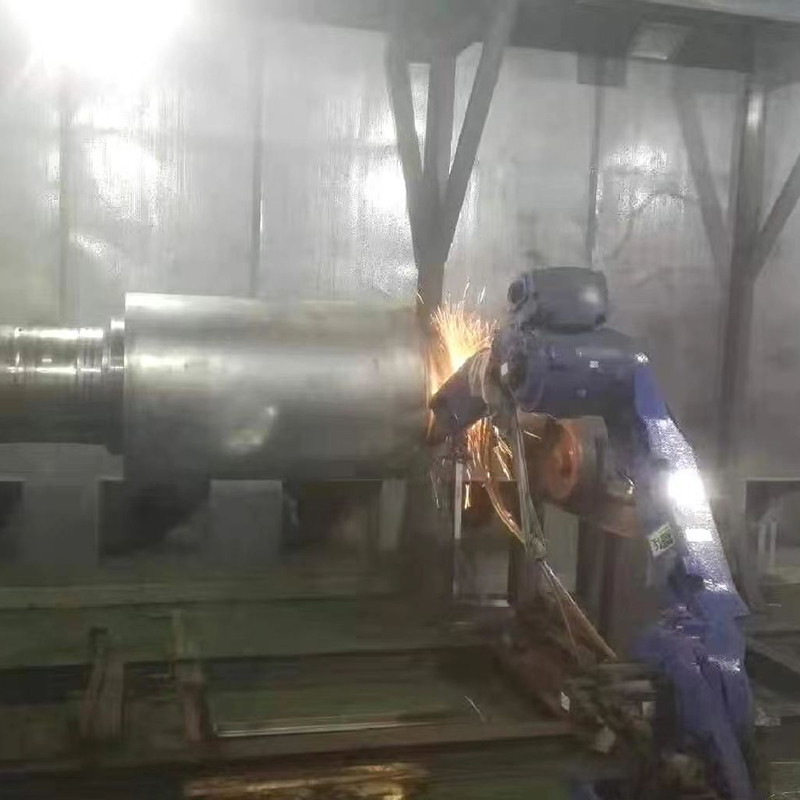
Abrasion resistant coating is a surface treatment designed to protect substrates from mechanical wear caused by friction, impact, or repeated contact with abrasive materials. These coatings are widely applied to metals, plastics, and composites to extend service life and maintain surface integrity in demanding operating environments. Rather than altering the base material, the coating acts as a protective layer that absorbs or resists wear during use.
How Abrasion Resistant Coatings Reduce Surface Wear
Abrasion resistant coatings work by increasing surface hardness or improving the ability of the surface to dissipate frictional forces. Depending on the formulation, the coating may contain ceramic particles, polymers, or metallic compounds that create a dense and durable barrier. This barrier minimizes material loss when the surface is exposed to sliding, scraping, or particle erosion.
Common Wear Mechanisms Addressed
Different abrasion resistant coatings are engineered to address specific wear mechanisms, such as sliding abrasion from continuous motion, impact abrasion from repeated strikes, or erosion caused by flowing particles. Selecting the correct coating requires understanding how and where wear occurs in the application.
Types of Abrasion Resistant Coating Materials
Abrasion resistant coatings are available in various material systems, each offering distinct performance characteristics. The choice of material depends on operating conditions such as load, temperature, and exposure to chemicals or moisture.
- Ceramic-based coatings for high hardness and severe wear environments
- Polymer-based coatings for flexibility and impact resistance
- Metallic and composite coatings for balanced strength and durability
Performance Factors That Influence Coating Effectiveness
The effectiveness of an abrasion resistant coating is influenced by several factors beyond material selection. Surface preparation, coating thickness, and application method all play critical roles in determining final performance. Poor adhesion or uneven coating can lead to premature failure even when high-quality materials are used.
Environmental and Operating Conditions
Temperature fluctuations, exposure to moisture, and contact with chemicals can affect coating durability. Some coatings are optimized for dry abrasion, while others maintain performance under wet or chemically aggressive conditions. Matching the coating to the real operating environment is essential for long-term reliability.
Typical Applications of Abrasion Resistant Coatings
Abrasion resistant coatings are used across a wide range of industries to protect components exposed to wear. These coatings help reduce maintenance frequency, prevent unexpected failures, and improve overall equipment efficiency.
- Industrial machinery components such as chutes, rollers, and housings
- Automotive and transportation parts subject to friction and debris
- Construction and mining equipment operating in abrasive environments
Comparing Coated and Uncoated Surfaces
| Aspect | With Abrasion Resistant Coating | Without Coating |
| Wear Rate | Significantly reduced | High material loss over time |
| Maintenance Frequency | Lower, extended service intervals | Frequent repairs or replacement |
| Surface Integrity | Maintained under abrasive conditions | Rapid surface degradation |
Practical Considerations When Selecting a Coating
When selecting an abrasion resistant coating, it is important to balance wear resistance with other requirements such as flexibility, adhesion, and compatibility with the substrate. Overly hard coatings may crack under impact, while softer coatings may wear too quickly in high-friction applications. A practical evaluation of operating conditions helps achieve optimal performance.
Conclusion
Abrasion resistant coating plays a critical role in protecting components exposed to mechanical wear. By reducing surface damage, extending service life, and lowering maintenance demands, these coatings provide tangible benefits across industrial, automotive, and construction applications. Proper material selection and application practices are key to achieving reliable and long-lasting wear protection.

 ENG
ENG
 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体












 TOP
TOP