Content
Overview of Ceramic Thermal Spray Coatings
Ceramic thermal spray coatings are advanced surface engineering solutions applied to protect metal, ceramic, or composite substrates from extreme conditions. These coatings provide enhanced wear resistance, corrosion protection, thermal insulation, and chemical stability. Their versatility makes them widely used in aerospace, automotive, power generation, and industrial machinery applications.
The effectiveness of ceramic thermal spray coatings depends on the proper selection of both spraying techniques and coating materials. Understanding the methods and materials involved is essential for achieving long-lasting, high-performance protective layers.
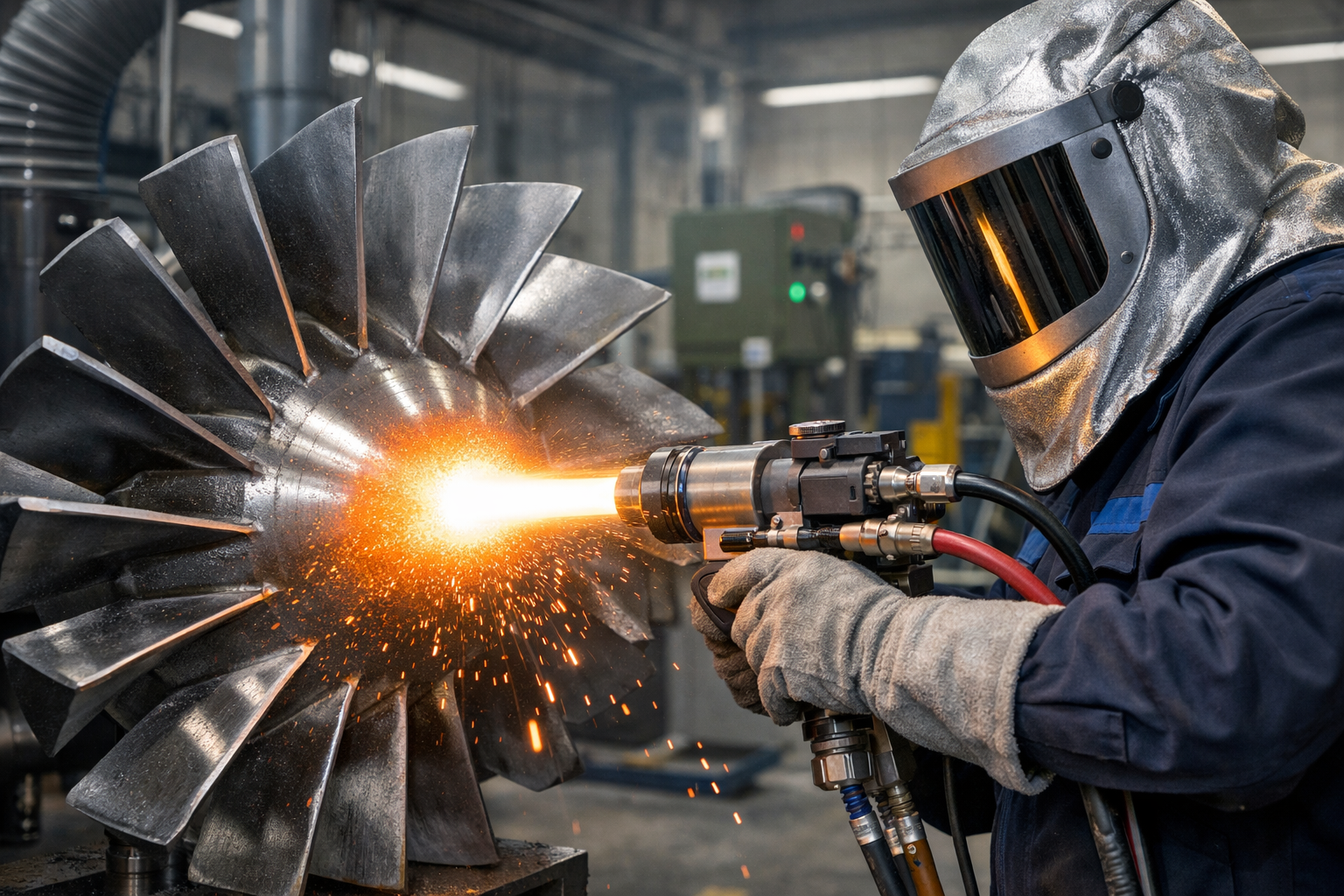

Common Techniques for Applying Ceramic Thermal Spray Coatings
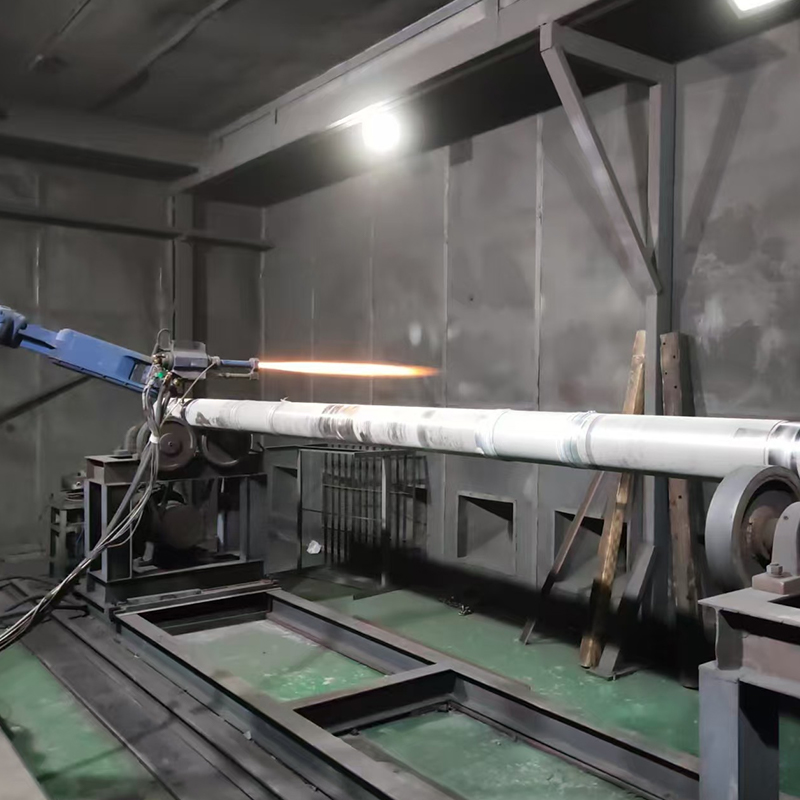
Several thermal spray techniques are used to deposit ceramic coatings onto substrate surfaces. Each technique has unique advantages, depending on the application requirements, substrate material, and desired coating properties.
Plasma Spraying
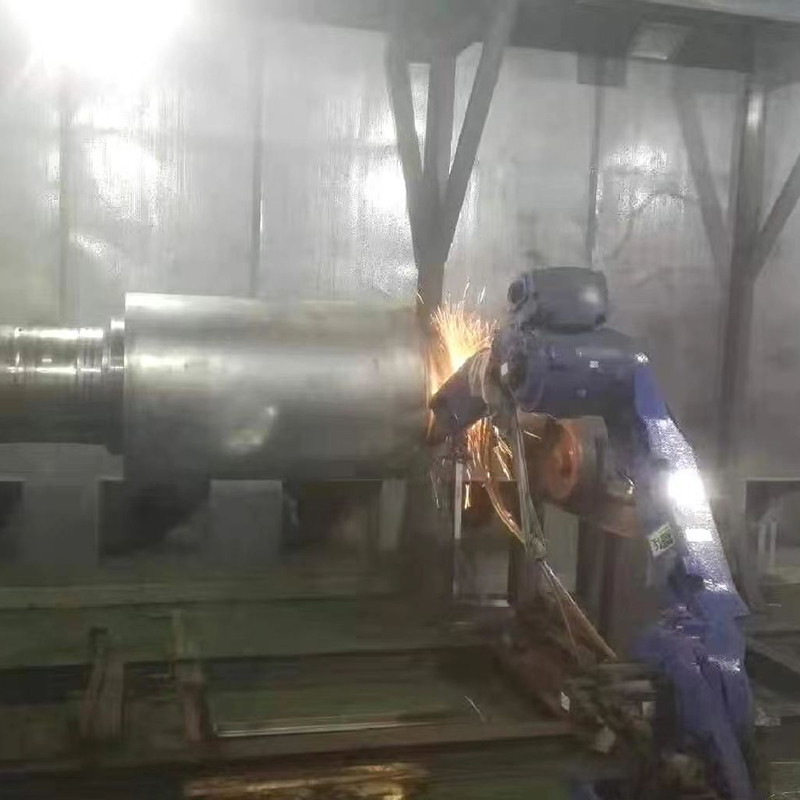
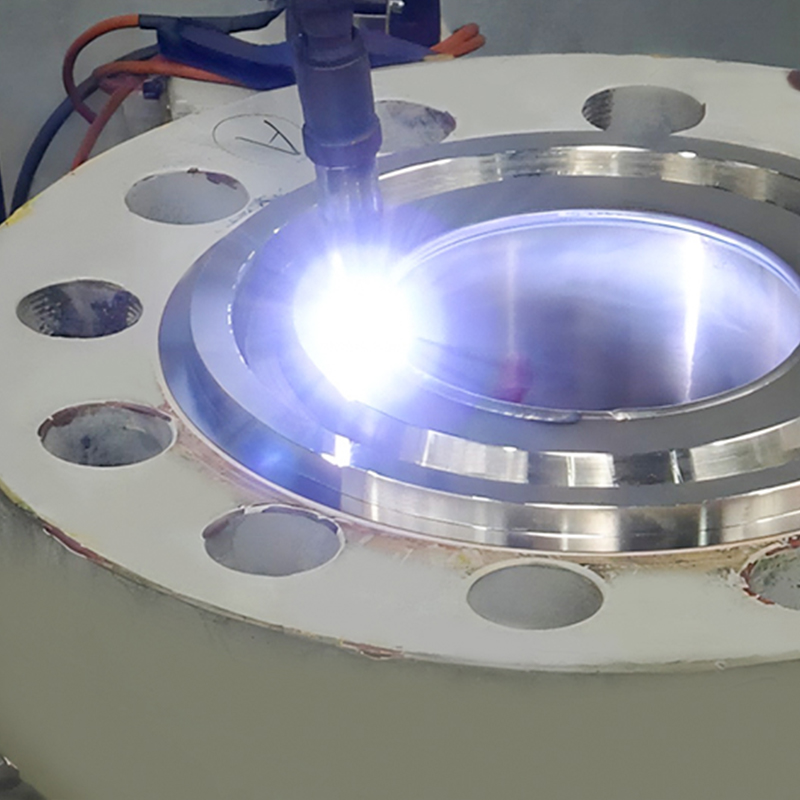
Plasma spraying uses a high-temperature plasma jet to melt ceramic powders before they are propelled onto the substrate surface. This method produces dense coatings with excellent adhesion and uniformity, suitable for high-temperature applications such as turbine blades and industrial furnaces.
- Capable of depositing high-melting-point ceramics like alumina, zirconia, and yttria-stabilized zirconia.
- Produces coatings with high hardness and wear resistance.
- Allows control of coating thickness and microstructure.
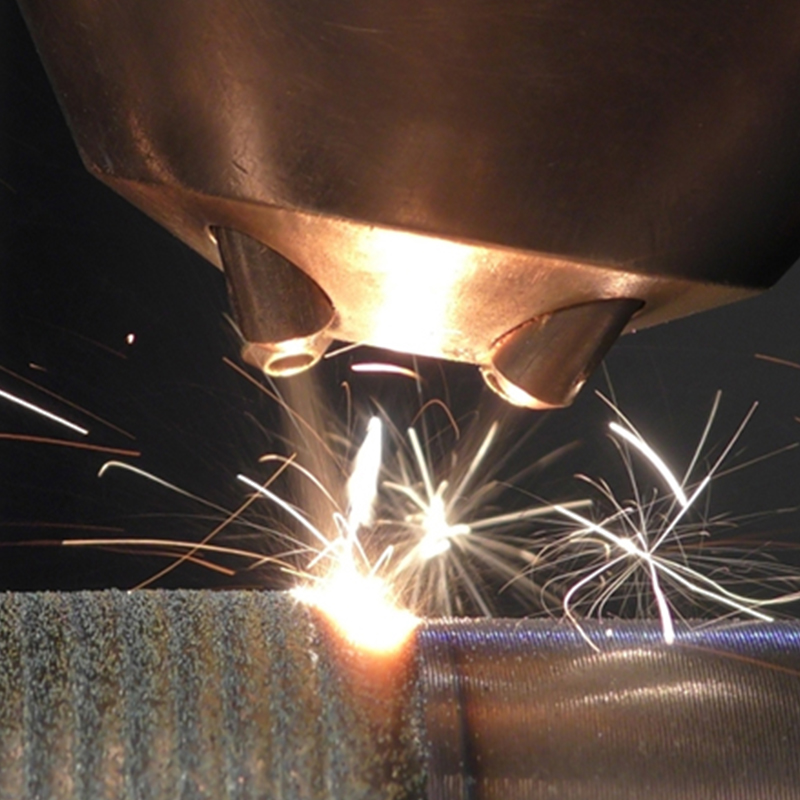
High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spraying
HVOF spraying propels molten or semi-molten ceramic particles at supersonic speeds toward the substrate using a high-pressure oxygen-fuel combustion system. This technique produces extremely dense coatings with low porosity and strong adhesion, ideal for wear and corrosion resistance in industrial machinery and pipelines.
- Offers excellent bonding strength between ceramic particles and substrate.
- Minimizes oxide formation and coating defects.
- Suitable for protective layers on shafts, valves, and pumps.
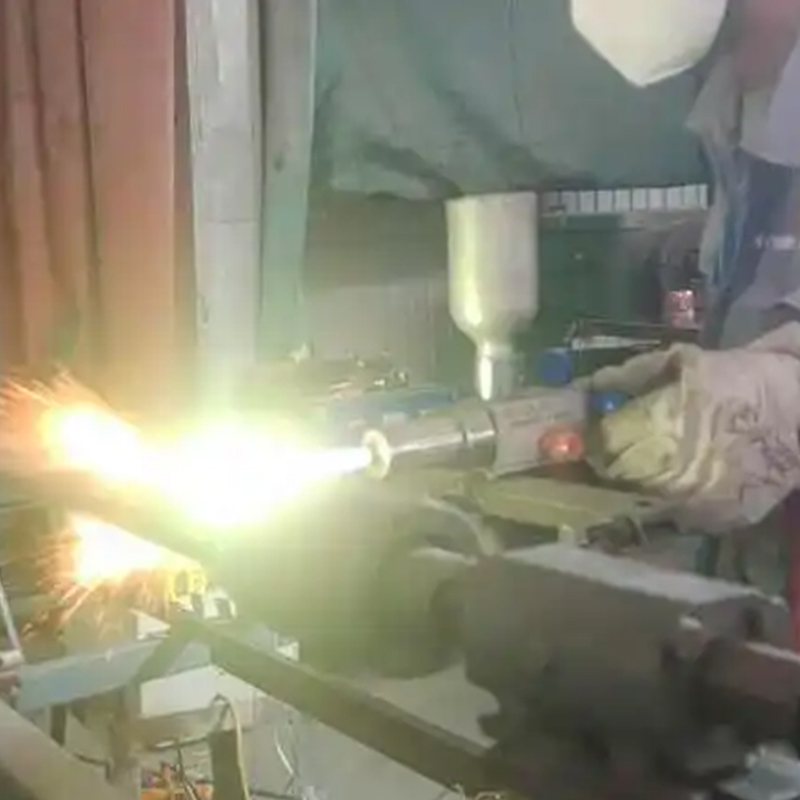
Flame Spraying
Flame spraying uses a fuel-oxygen flame to melt ceramic powders, which are then sprayed onto the substrate with compressed gas. While this method may produce coatings with slightly higher porosity than plasma or HVOF, it is cost-effective and widely used for moderate wear and thermal protection applications.
- Applicable for coatings on large surface areas.
- Compatible with various ceramic powders and metal-ceramic composites.
- Easily scalable for industrial production.
Materials Used in Ceramic Thermal Spray Coatings
The selection of ceramic materials directly affects the performance characteristics of the coating, such as hardness, thermal conductivity, and resistance to oxidation or corrosion. Different applications demand specific materials to meet operational requirements.
Alumina (Al2O3)
Alumina is one of the most commonly used ceramics for thermal spray coatings. It provides excellent wear resistance, electrical insulation, and moderate thermal protection. Alumina coatings are suitable for pumps, valves, and chemical process equipment.
Zirconia (ZrO2)
Zirconia, often stabilized with yttria, offers outstanding thermal barrier properties, high fracture toughness, and resistance to thermal cycling. Zirconia coatings are widely applied in gas turbines, combustion engines, and heat exchangers where high-temperature performance is critical.
Titania (TiO2)
Titania provides moderate hardness, chemical stability, and enhanced wear resistance. It is often used in combination with other ceramics to improve bonding, reduce porosity, and provide cost-effective protective coatings for mechanical parts and industrial machinery.
Composite Ceramics
Composite ceramic coatings combine two or more ceramic materials or integrate metals to enhance specific properties. For example, alumina-titania composites improve toughness and reduce brittleness, while metal-ceramic composites enhance adhesion and thermal conductivity.
- Alumina-titania for improved toughness and wear resistance.
- Metal-ceramic composites for enhanced bonding and thermal shock resistance.
- Customized compositions tailored for specific industrial applications.
Comparison of Thermal Spray Techniques
| Technique | Coating Density | Surface Finish | Ideal Applications |
| Plasma Spray | High | Smooth, uniform | Turbines, furnaces |
| HVOF | Very High | Dense, low porosity | Shafts, pumps, valves |
| Flame Spray | Moderate | Moderate | Large surfaces, moderate wear |
Conclusion
Choosing the right technique and material for ceramic thermal spray coatings is essential for optimizing performance in industrial applications. Plasma, HVOF, and flame spraying offer distinct advantages in terms of density, adhesion, and surface finish, while materials such as alumina, zirconia, titania, and composites provide tailored properties for wear resistance, thermal protection, and chemical stability. By understanding these factors, engineers and manufacturers can apply coatings effectively to enhance equipment durability, reduce maintenance costs, and extend service life.

 ENG
ENG
 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体












 TOP
TOP