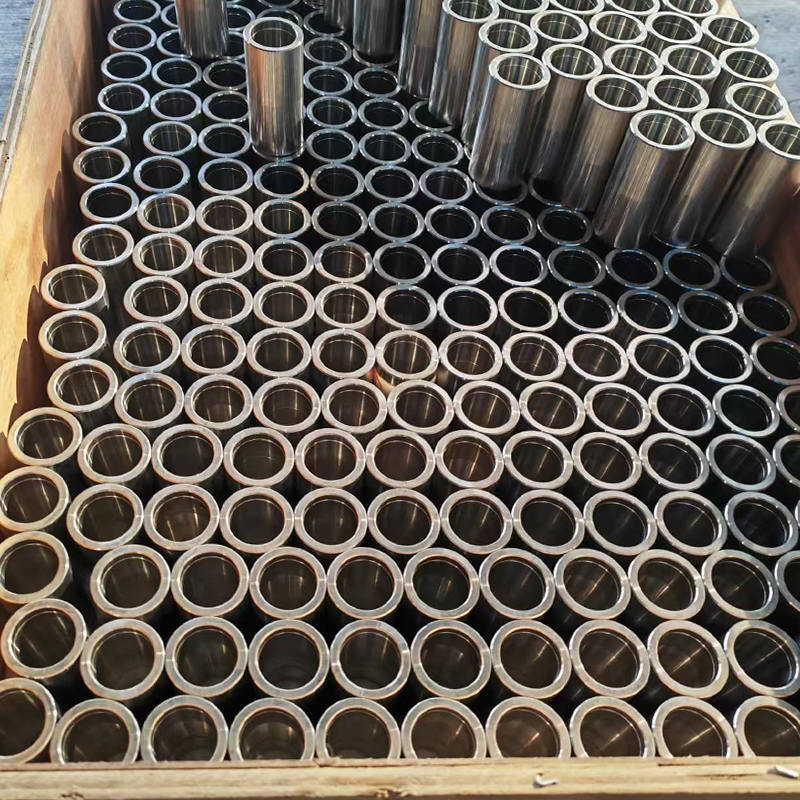
Coated shaft sleeves play a critical role in reducing maintenance frequency and overall operating costs in industrial equipment. By providing enhanced surface hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear protection, these sleeves extend component life, reduce downtime, and minimize labor and replacement costs. Understanding the mechanisms behind these benefits helps engineers and plant managers select the most suitable sleeve coatings for their applications.
Content
Wear reduction through advanced coatings
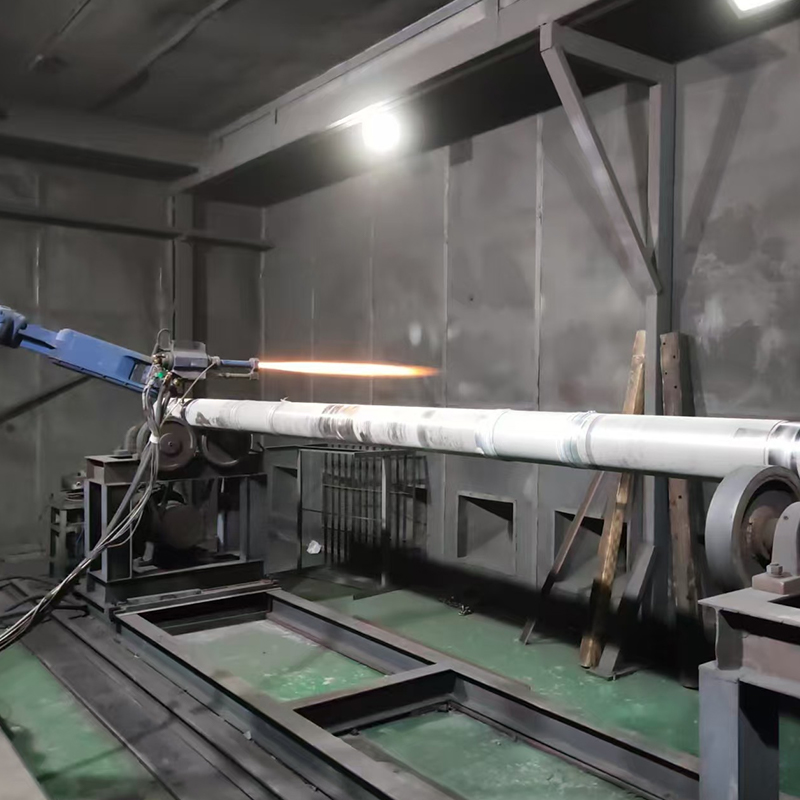
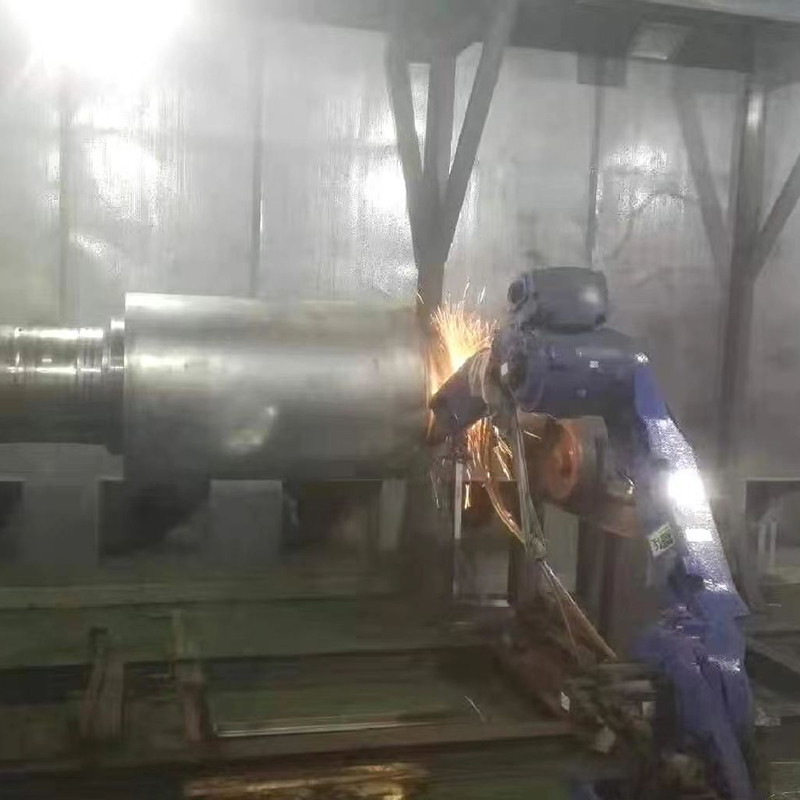
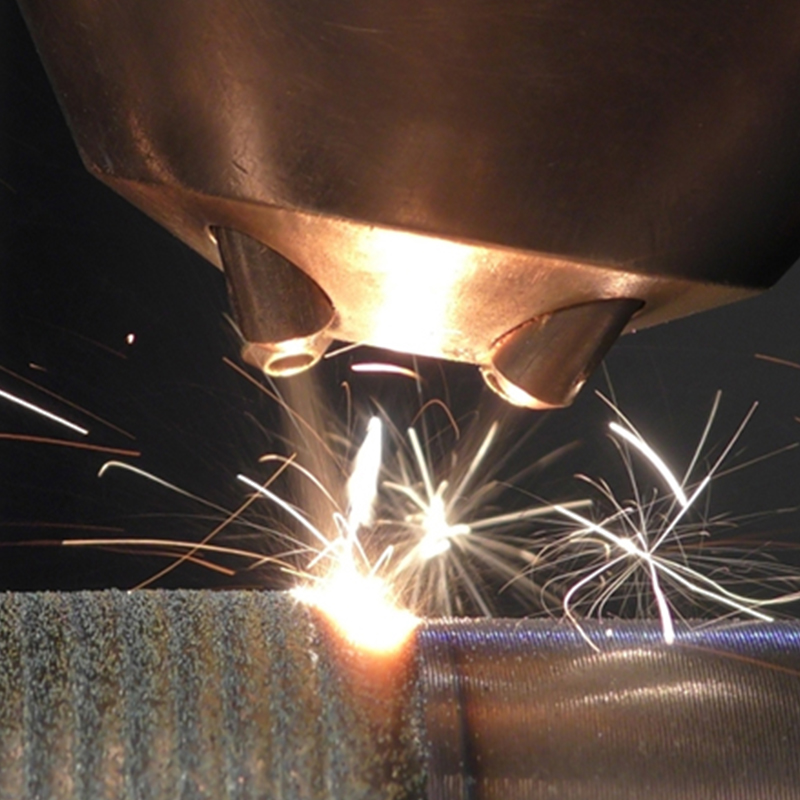
The primary function of coated shaft sleeves is to resist wear from abrasive particles, friction, and repeated mechanical contact. Coatings such as hard chrome, thermal spray ceramics, or tungsten carbide composites create a durable surface layer that reduces metal-to-metal contact, limiting scoring and grooving. Less wear translates directly into fewer maintenance interventions and longer intervals between component replacements.

Benefits for rotating machinery
In pumps, mixers, and turbines, even minor shaft wear can lead to seal failures and vibration issues. A coated shaft sleeve preserves the original shaft geometry, maintaining tight tolerances for mechanical seals and bearings. This reduces unplanned stoppages and prevents costly cascading failures in connected systems.
Corrosion protection and chemical resistance
Many industrial environments expose shaft sleeves to corrosive fluids or high-humidity conditions. Coatings such as stainless steel overlays, nickel-based alloys, or ceramic layers prevent surface corrosion and pitting. By limiting degradation, these coatings reduce the need for frequent inspections, re-machining, or premature sleeve replacement, cutting long-term operating expenses.
Applications in chemical processing
Chemical pumps and agitators benefit from coated sleeves that withstand acidic or alkaline media. Coated sleeves maintain seal integrity and prevent leaks, reducing downtime for cleaning, repair, or seal replacement. This directly improves plant efficiency and lowers labor costs.
Friction reduction and energy efficiency
Low-friction coatings reduce heat generation and mechanical resistance in rotating shafts. By minimizing energy loss and wear, these coatings decrease the frequency of lubrication cycles and help maintain stable operating parameters. Reduced energy consumption and fewer maintenance tasks contribute to lower overall operating costs.
Enhanced sealing performance
A smooth, wear-resistant coated surface ensures consistent contact with mechanical seals. This reduces the likelihood of leaks, extends seal life, and minimizes the need for emergency maintenance. For high-speed applications, the stability of the coated sleeve prevents vibration-induced seal damage, improving reliability and lowering replacement costs.
Maintenance and inspection advantages
Coated shaft sleeves simplify maintenance schedules by extending service intervals. They allow condition-based inspections rather than fixed-time replacements, enabling predictive maintenance strategies. Fewer emergency repairs mean less downtime, lower spare part inventory, and reduced labor costs, all contributing to a more cost-efficient operation.
Inspection-friendly design
Many coated sleeves are designed with smooth, visible surfaces that facilitate quick visual inspections for wear or corrosion. This reduces the need for disassembly and allows maintenance teams to identify potential issues before they escalate, preventing expensive equipment failures.
Cost comparison: coated vs uncoated sleeves
| Feature | Uncoated Sleeve | Coated Sleeve |
| Wear resistance | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance frequency | High | Low |
| Seal life | Short | Extended |
| Energy efficiency | Moderate | Improved |
| Overall operating cost | Higher | Lower |
Conclusion
Coated shaft sleeves provide multiple mechanisms for reducing maintenance frequency and operating costs. By improving wear resistance, corrosion protection, friction behavior, and seal compatibility, these sleeves extend service life and reduce unplanned downtime. Properly selected coatings allow operators to implement predictive maintenance strategies, minimize spare part requirements, and achieve significant cost savings over the equipment lifecycle.

 ENG
ENG
 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体












 TOP
TOP