Content
- 1 Understanding Abrasion Resistant Coating Fundamentals
- 2 Common Materials Used in Abrasion Resistant Coatings
- 3 Abrasion Mechanisms and Their Impact on Coating Performance
- 4 Key Performance Characteristics of Abrasion Resistant Coatings
- 5 Surface Preparation and Application Considerations
- 6 Industrial Uses of Abrasion Resistant Coatings
- 7 Evaluating Abrasion Resistant Coating Selection
Understanding Abrasion Resistant Coating Fundamentals
Abrasion resistant coating refers to a category of surface protection materials designed to reduce material loss caused by friction, impact, and repetitive contact with hard particles. These coatings are commonly applied to metal, concrete, and composite substrates exposed to sliding wear, particle erosion, or mechanical scraping. Instead of changing the base material, abrasion resistant coatings provide a sacrificial or reinforced surface layer that absorbs wear and delays substrate damage.
In industrial environments, abrasion is often unavoidable due to material handling, bulk transport, and continuous mechanical movement. Abrasion resistant coatings address this issue by improving surface hardness, toughness, or elasticity depending on the wear mechanism involved. Their performance depends on coating composition, thickness, adhesion strength, and compatibility with operating conditions.
Common Materials Used in Abrasion Resistant Coatings
Abrasion resistant coatings are formulated using different material systems, each suited to specific wear environments. The choice of material directly affects hardness, impact resistance, chemical stability, and service life.
- Ceramic-based coatings provide high hardness and strong resistance to particle erosion, often used in severe abrasive environments.
- Polymer-based coatings, including epoxy and polyurethane systems, offer flexibility and impact resistance where vibration or deformation occurs.
- Metal-filled coatings combine metallic particles with binders to improve load-bearing capacity and thermal stability.
- Carbide-reinforced coatings enhance wear resistance under sliding and gouging abrasion conditions.
Selecting coating materials requires matching the coating structure to the dominant abrasion type rather than focusing only on hardness values.
Abrasion Mechanisms and Their Impact on Coating Performance
Different abrasion mechanisms affect coatings in distinct ways. Understanding these mechanisms helps determine coating suitability and expected lifespan.
| Sliding Abrasion | Caused by surfaces moving against each other under load | Conveyors, guide rails, wear plates |
| Erosive Abrasion | Resulting from high-velocity particles impacting the surface | Chutes, pipelines, fans |
| Gouging Abrasion | Severe material removal from large hard particles | Crushers, mining buckets |
A coating optimized for sliding abrasion may perform poorly under impact-driven erosion, making abrasion analysis a critical step in coating selection.
Key Performance Characteristics of Abrasion Resistant Coatings
Abrasion resistance alone does not define coating effectiveness. Several performance characteristics work together to determine real-world durability.
- Hardness influences resistance to scratching and cutting by abrasive particles.
- Adhesion strength ensures the coating remains bonded under repeated stress.
- Impact resistance prevents cracking or spalling during mechanical shock.
- Chemical stability maintains coating integrity in corrosive or wet environments.
Balancing these properties allows coatings to perform consistently across variable operating conditions rather than excelling in only one aspect.
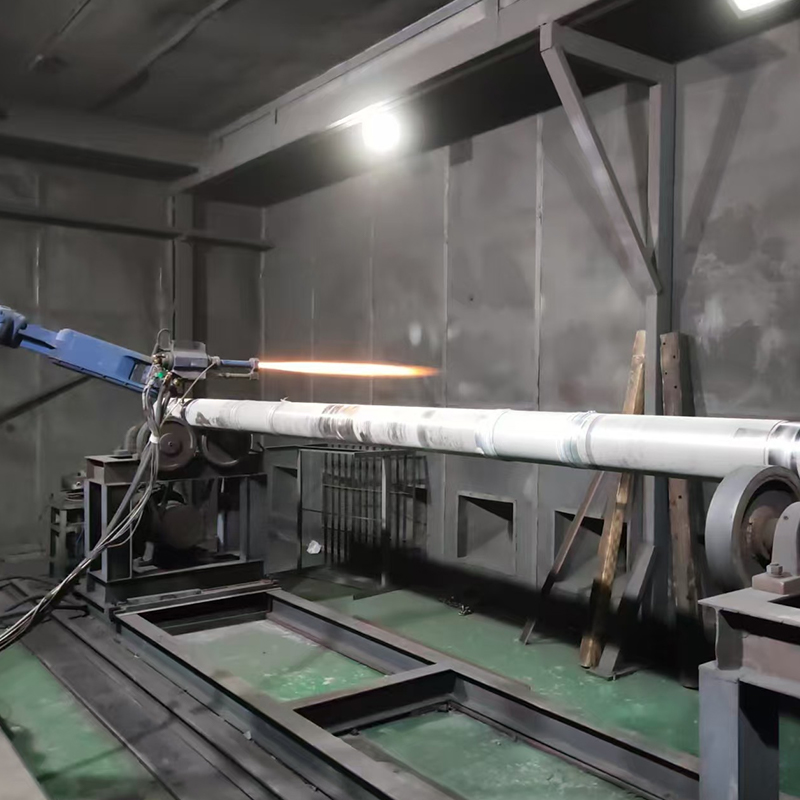
Surface Preparation and Application Considerations
Proper surface preparation plays a major role in abrasion resistant coating performance. Inadequate preparation often leads to premature failure regardless of coating quality.
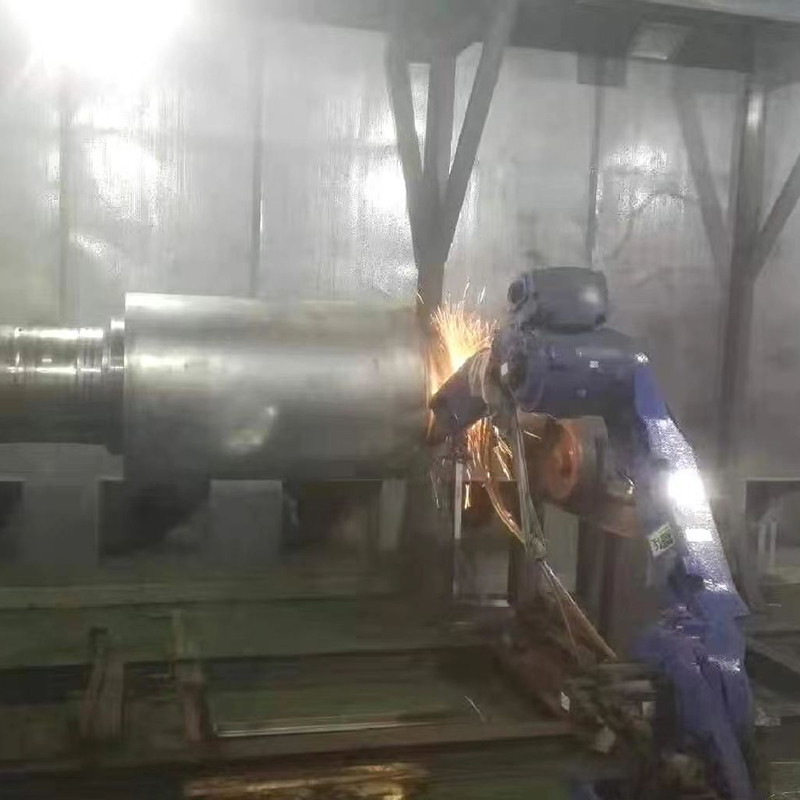
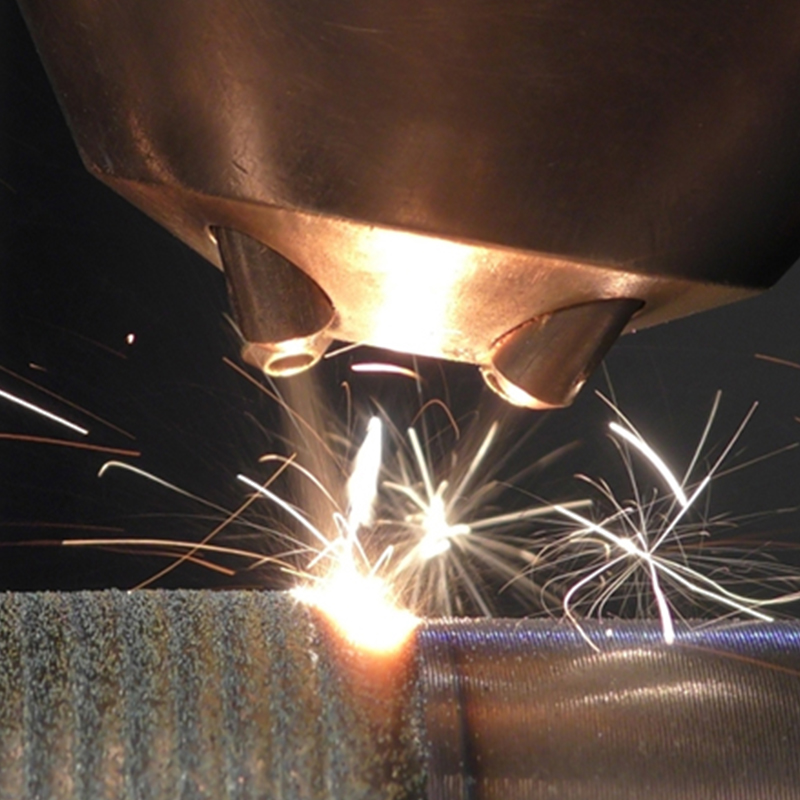
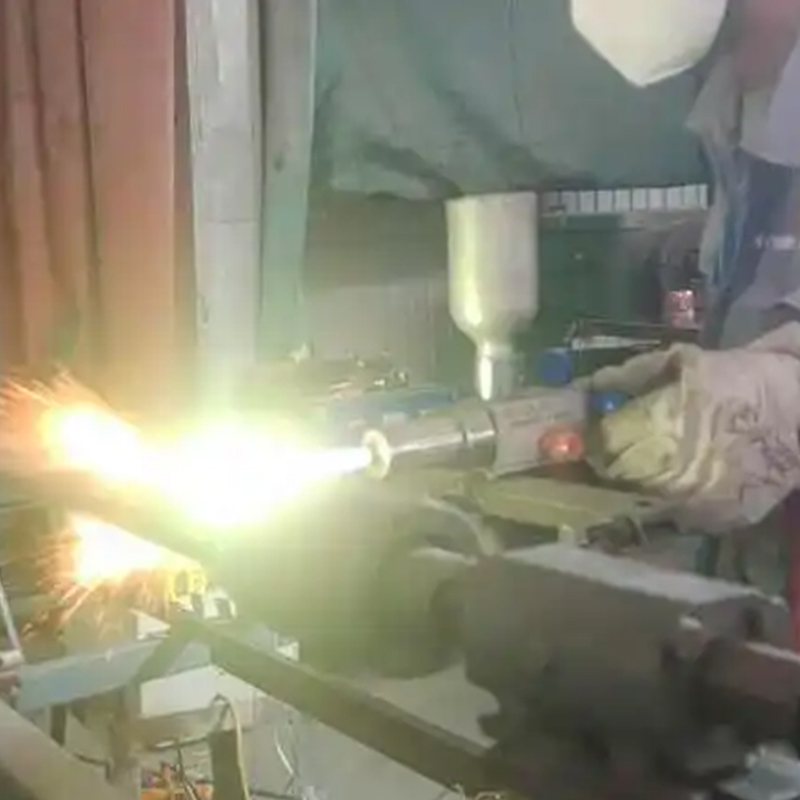
Typical preparation methods include abrasive blasting, degreasing, and surface profiling to achieve sufficient roughness for mechanical bonding. Application methods such as spraying, troweling, or brushing are selected based on coating viscosity, thickness requirements, and component geometry.
Controlled curing conditions further influence final coating properties, especially for polymer-based systems where temperature and humidity affect cross-linking behavior.
Industrial Uses of Abrasion Resistant Coatings
Abrasion resistant coatings are widely used across industries where material wear leads to frequent maintenance or downtime. Their application reduces surface damage and stabilizes operating performance.
- Mining and quarrying equipment such as chutes, hoppers, and liners
- Bulk material handling systems including conveyors and transfer points
- Cement and power plants exposed to continuous particle flow
- Industrial pipelines subjected to slurry or solid-laden fluids
By targeting high-wear zones, coatings help extend component service intervals without redesigning the entire system.
Evaluating Abrasion Resistant Coating Selection
Selecting an abrasion resistant coating requires evaluation of wear type, operating temperature, mechanical stress, and maintenance strategy. A coating that aligns with actual service conditions delivers more consistent performance than one chosen solely by laboratory abrasion data.
Long-term value is achieved when coating performance, application feasibility, and maintenance planning are considered together, allowing abrasion resistant coatings to function as part of an integrated wear management approach.

 ENG
ENG
 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体












 TOP
TOP